To harvest energy
Biophotovoltaic Moss Table

Carlos Peralta, Alex Driver, Paolo Bombelli
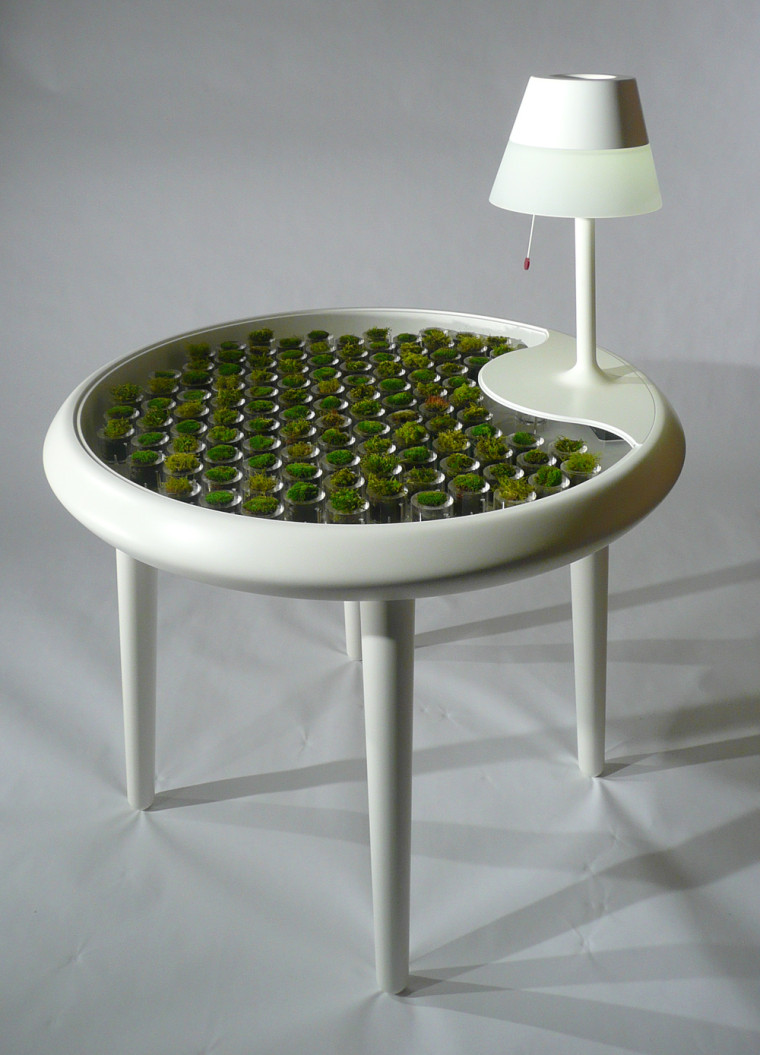
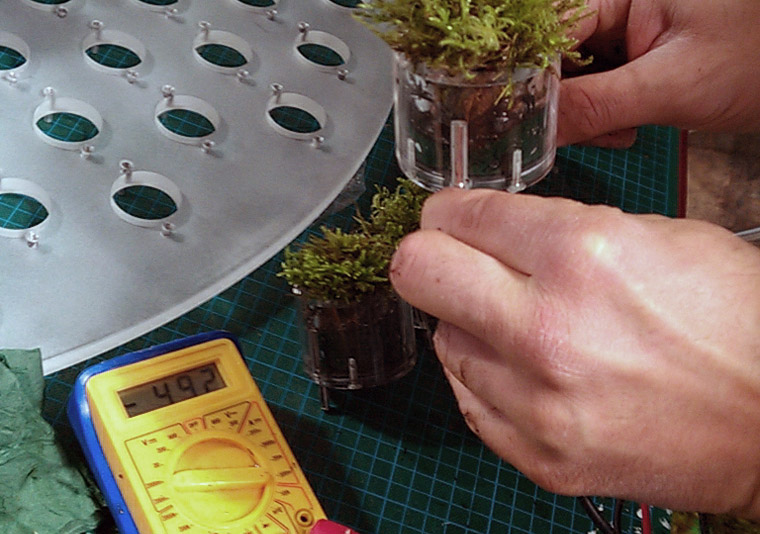
The ‘Moss Table’ is a conceptual design intended to illustrate the potential of biophotovoltaic technology and how it might be applied in the future. Biophotovoltaic (BPV) devices generate renewable energy and other useful by-products from the photosynthesis process in living organisms such as algae and moss. The ‘Moss Table’ suggests a future in which hybrid natural/artificial objects are utilised in the home. Biophotovoltaic technology is at a very early stage of development. Moss can be used to power small electronic devices like a digital alarm clock, but cannot currently power the table’s integrated lamp. However scientists anticipate that with further research, applications like this may be feasible. Low-cost BPV devices may become competitive alternatives to conventional renewable technologies such as bio-fuels in the future.

The ‘Moss Table’ suggests a future in which hybrid natural/artificial objects are utilised in the home.
The ‘Moss Table’ is an output of the Design in Science research project at Cambridge University’s Institute for Manufacturing. Biophotovoltaics research involves the departments of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, Biochemistry and Plant Sciences at Cambridge University, and the Chemistry department at Bath University. Both research projects are funded by the EPSRC.